Blog

Pivot Table in Python¶
What is Pivot Table¶
Pivot Table is one of the most efficient functionalities which we generally used in the Microsoft Excel or Google Spreadsheet or any other similar program. Pivot Table is used for summarizing the data in various ways with respect to the attributes available in the data. You can also add some formulas and calculations to it.
Pivot Table in Excel¶
We are going to use Superstore Sales Dataset available in Kaggle. To get this dataset Click Here. If we use the pivot table in Excel, then It would look like below. It will have four fields to play with.
- Filters – Filter the data used in the other 3 fields
- Columns – Defining columns of summarized data
- Rows – Defining rows of summarized data
- Values – Summary Statistics like Sum, Count, Average, % etc.
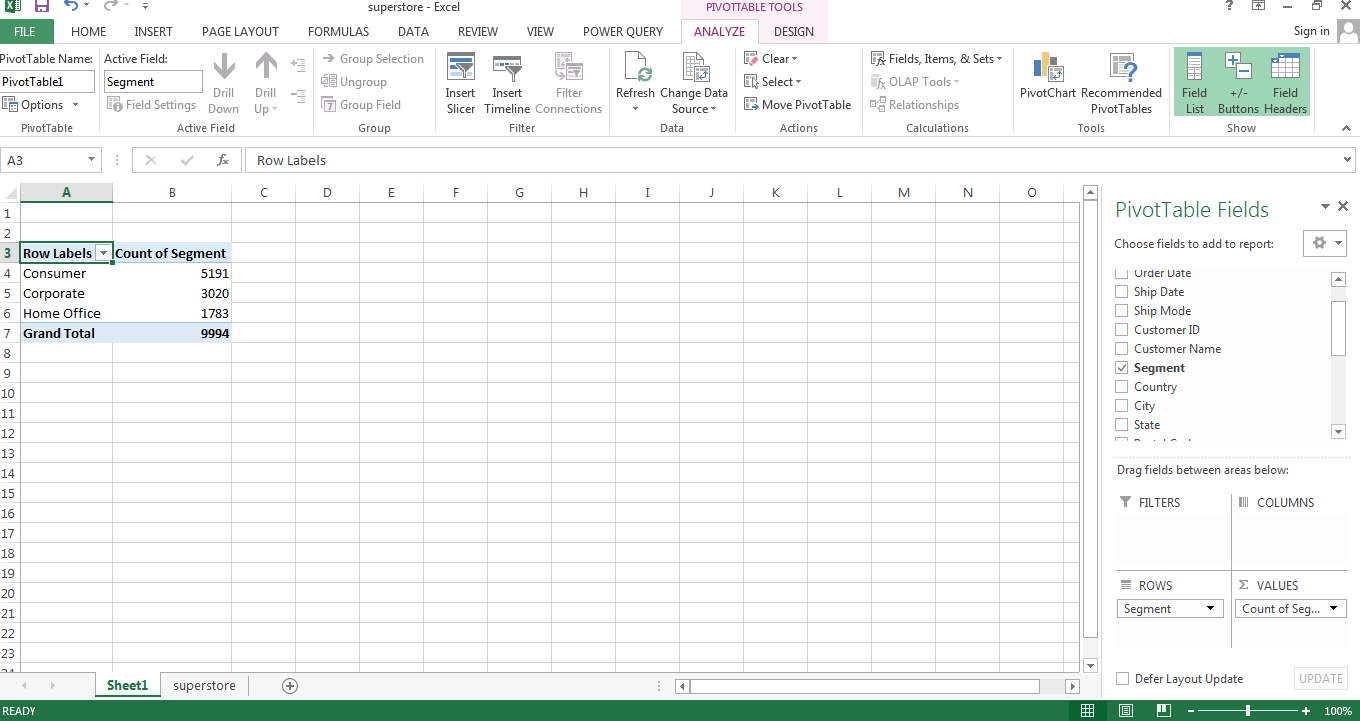
If we want to summarize Segments with its count, then we shall drag and drop the Segment field in Rows because we want to summarize the Segment field. We shall drag again Segment field to Values because we want counts in each segment. It is shown in the below image.
Pivot Table in Python¶
In python, Pivot table functionality is also available. It is in the Pandas library. It is the most efficient library developed for data manipulation and analysis on programming languages like Python. To know more about Pandas, Click Here.
We will also use Numpy library as it is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. It contains among other things:
- a powerful N-dimensional array object
- sophisticated (broadcasting) functions
- tools for integrating C/C++ and Fortran code
- useful linear algebra, Fourier transform, and random number capabilities
# Importing Library
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Importing Dataset and store it in the object df
df = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\\Neerav\\superstore.csv")
# Print first 5 rows of data
df.head()
Let’s say, we want Average Sales, with respect to Category and Segment. We want Segment in Columns and Category in rows.
In Pivot Table function, first argument is Dataset. Here our data is stored in “df”. Second argument is summary variable, here it is “Sales”. Third argument is variable for Rows. Here it is “Category”. Fourth argument is variable for Columns. Here it is “Segment”. And the fifth argument is of aggfunc (aggregate function) in which we can mention how we want to summarize our data like Sum, Average, Count etc.
pd.pivot_table(df, "Sales", "Category", "Segment", aggfunc=np.mean)
Now if we want wan to add Overall Column and Rows at the end. Then we can add argument margins = True. By default, it will have column and row name as “All”. But if we want to give custom name, then we can add an argument margins_name=”Overall_Average”.
pd.pivot_table(df, "Sales", "Category", "Segment", aggfunc=np.mean, margins=True, margins_name="Overall_Average")
Life is not that simple. Sometimes we want another categorical variable in rows or columns to make more eloborative summary of the data. For example, here in this case we want “ship mode” to be added in to the Rows. So how can we do that?
pd.pivot_table(df, "Sales", ["Ship Mode", "Category"], "Segment", aggfunc=np.mean, margins=True, margins_name="Overall_Average")
Similarly, if we want to put this in column instead of row. Then we can put it in the third argument.
pd.pivot_table(df, "Sales", "Category", ["Segment", "Ship Mode"], aggfunc=np.mean)
Hope this is helpful to you. Please mention you queries to comment box. Also let us know, on which topic you want us to write next blog.
